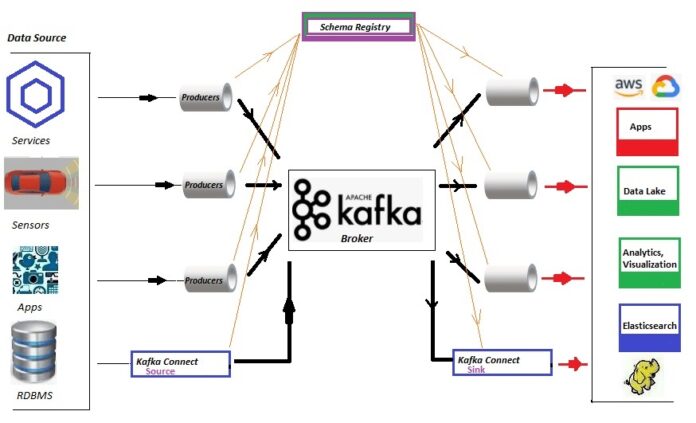
In today’s data-driven landscape, organizations are continually on the lookout for platforms and tools that can manage, transport, and make sense of vast volumes of data. Central to this journey is the big data architectural concept of a “data lake” – a vast reservoir that holds a vast amount of raw data in its native format.
But the question arises: how do you efficiently and consistently feed data into these massive storage entities? Enter Apache Kafka. For those pondering over “what is Kafka used for?”, it serves as a real-time, fault-tolerant, and highly scalable event streaming platform, designed to seamlessly transport huge streams of data into systems like data lakes. In the intricate dance of big data, while data lakes provide the stage, Kafka emerges as a lead performer, choreographing the flow of data with precision.
This article delves deep into the symbiotic relationship between Kafka and data lakes, highlighting how Kafka streamlines big data architectures and enhances the efficiency of data lakes.
Understanding Data Lakes
A Data Lake is essentially a vast storage repository, designed to hold a massive amount of raw data in its native format until it’s needed. This is in stark contrast to traditional data warehouses, which store structured data in a processed format. While data warehouses are more like bottled water, curated and processed, data lakes are akin to natural reservoirs, holding both pristine streams and murky waters alike. The freedom to store data in a raw, unaltered state is both the strength and challenge of a data lake. Building an efficient one requires a sophisticated ingestion process, scalable storage, and advanced analytics capabilities.
Introduction to Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka, at its core, is an open-source stream-processing software platform. Designed by LinkedIn and donated to the Apache Software Foundation, Kafka is all about real-time data. It’s built on an event-driven architecture, making it exceptionally suitable for handling streaming data. Imagine Kafka as a high-speed train, capable of transporting vast amounts of passengers (or in this case, data) across various destinations seamlessly. Its efficiency lies in its ability to ingest, process, and move large volumes of data in real-time, making it a valuable player in the big data realm.
Kafka’s Role in Modern Big Data Architectures
Big data is not just about volume but velocity and variety. Kafka is adept at managing all three. With its capacity for real-time data ingestion and processing, Kafka has established itself as an invaluable tool in the big data toolkit. Its scalability ensures that as data inflows increase, Kafka can handle the influx without compromising on performance. Additionally, its fault-tolerance mechanisms ensure data integrity and availability. Kafka also plays well with others. Its integrative capabilities mean it can seamlessly connect with various big data tools, enhancing the data processing pipeline and enriching data lakes with diverse data streams.
Kafka and Data Lakes: A Perfect Partnership
In the ecosystem of big data, where data lakes play the role of storage giants, Kafka emerges as the efficient conduit that feeds these lakes. Kafka’s real-time data streaming capabilities are essential in ensuring that data lakes receive the constant flow of data they’re designed to store. And it’s not just about the speed; it’s about quality too. Kafka’s durability and replication features ensure that the data streaming into lakes is consistent and reliable.
Consider an e-commerce platform that’s dealing with millions of transactions every day. Each transaction, product search, user click, or cart addition represents a piece of data. To gain insights from this data, it’s crucial to collect, process, and store it efficiently. Here, Kafka can capture the real-time data generated, process it, and then pour it into a data lake for further analysis. This synergistic relationship ensures that businesses can make the most of their data, deriving actionable insights and improving their strategies.
Advantages of Leveraging Kafka with Data Lakes
- Real-time Data Ingestion: Kafka’s prowess in real-time data streaming ensures that data lakes are always updated with the most recent data, allowing businesses to make decisions based on real-time insights.
- Scalability: Both Kafka and data lakes are designed to handle vast amounts of data. As business data needs grow, Kafka’s distributed nature ensures it can handle increased loads, ensuring data lakes are continuously fed without bottlenecks.
- Data Integrity: Kafka’s fault tolerance and data durability features ensure that the data flowing into data lakes is reliable and consistent.
- Flexibility: Kafka can integrate with various big data tools and platforms, ensuring that data lakes can be populated with a variety of data types from different sources.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
While Kafka presents numerous advantages, like any technology, it’s not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is ensuring that the vast streams of data remain ordered and timely. Out-of-order data can lead to inconsistencies, especially in real-time analytics scenarios. To address this, Kafka offers features like maintaining topic partitions. Another challenge is data retention. With the vast inflows, ensuring older data is appropriately managed and doesn’t clog the system is crucial. Here, Kafka’s log compaction feature proves beneficial, ensuring that older data can be efficiently managed without compromising system performance.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Kafka and Data Lakes
The world of big data is rapidly evolving, and the partnership between Kafka and data lakes appears to be growing stronger. As businesses continue to recognize the importance of real-time analytics and the value of comprehensive, raw data repositories, the synergy between Kafka and data lakes will only intensify. There’s also a growing trend towards cloud-native data lakes, and Kafka’s compatibility with cloud environments indicates a future where they both play pivotal roles in the next generation of big data solutions.
Conclusion
In the vast universe of big data, where data lakes represent the vast galaxies of raw information, Kafka emerges as the comet, streaking through space, delivering timely data to these reservoirs. The relationship between Kafka and data lakes isn’t just about storage and transport; it’s about maximizing the potential of real-time data, ensuring businesses can glean timely insights, adapt strategies, and continue to thrive in an increasingly data-driven world. As we peer into the future of big data, the alliance of Kafka and data lakes offers promise, potential, and endless possibilities.
Read Also: Read The Best AMD Radeon R9 285 Review